What is arc flash?
Arc flash is a phenomenon in which a flashover of electric current leaves its intended path and travels through the air from one conductor to another or the ground.¹ The extremely high temperature and pressure discharged when that electrical current travels through the air is an arc flash explosion. The high-pressure sound wave that occurs during the event is called an arc blast.
What causes an arc flash?
Generally, the cause of an arc flash explosion is a failure in the equipment, a surge or fault in the electrical system, or human error. Because none of these factors are predictable, anyone working on electrical assets must be aware of the inherent risks, required PPE, and the guidelines set by the NFPA (National Fire Prevention Association) and the European Agency for Safety and Health – OSH “Framework Directive.”
Arc flash causes include:
- Equipment failure
- A surge or fault in an electrical system
- Dropping un-insulated tools or metal parts
- The use of incorrect instruments, or the incorrect use of instruments
- Performing live work on faulty equipment
- Exposed live parts
- Human error
- Loose connections and exposed live parts
- Lack of training
How hot is an arc flash, and can you survive it?
An arc flash event can generate temperatures as high as 35,000 °F | 20,000 °C. How hot is that? For context, the sun’s surface is about 10,000 °F | 5,500 °C. While the highest temperature point of an arc flash may last a few seconds, it can cause extreme damage and injury.

- A lighting bolt is an extreme example of an arc flash in nature.
- As a lightning bolt’s electricity travels through the air, it can reach a temperature of up to 54,000 °F | 30,000 °C!
Can you survive an arc flash event?
There are important factors at play: the proximity of the individual to the arc flash, the arc fault’s energy, and the event’s duration before a protection mechanism interrupts the current. An arc flash can emit temperatures that ignite clothing and burn metal, causing burns and damage to the eyes and lungs. The sound and pressure of the blast can cause hearing damage. Lastly, the ultraviolet light produced in the explosion can cause eye damage and even blindness.
In short, depending on multiple factors, you could potentially survive an arc flash but risk injury and hospitalization.
How to prevent an arc flash?
The complete elimination of arc flash hazards is difficult unless the power supply is fully isolated. And while the likelihood of an electric arc occurring might be low, the potential consequences are severe.
Steps that can mitigate arc flash risk:
- Conduct or commission an arc flash study
- Wear appropriately rated PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
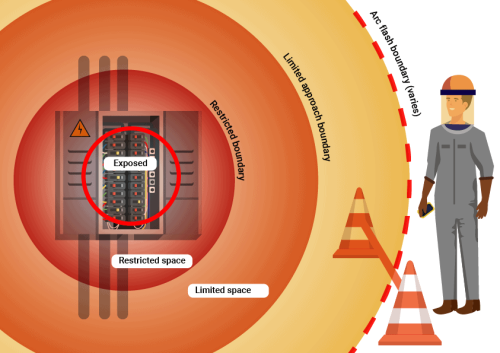
- Understand and follow flash protection boundaries
- Ensure arc flash labels are accurate and updated
- Develop and follow specific safe work practices
- Train workers to control risks and interrupt faults
- Consider arc flash relays to reduce incident energy
Download our updated SEAM Group Arc Flash PPE Poster with detailed information on protective clothing that meets current NFPA 70E standards.
What is an arc flash study?
The analysis of arc flash risks in a system and work environment is called an arc flash study, also known as an arc flash hazard analysis. The electrical engineering analysis looks at a facility’s electrical distribution system to determine the incident energy of a potential arc flash event and establish safety boundaries and PPE requirements. An arc flash study also produces arc flash warning labels affixed to individual pieces of equipment to document incident energy.
Arc flash studies must be performed every five years or whenever there are significant changes or updates to the electrical system, per OSHA and NFPA 70E.
Our trained, engineer-certified employees conduct your arc flash study with a high level of expertise, adhering to all safety procedures, wearing appropriate PPE, and communicating with you on progress.